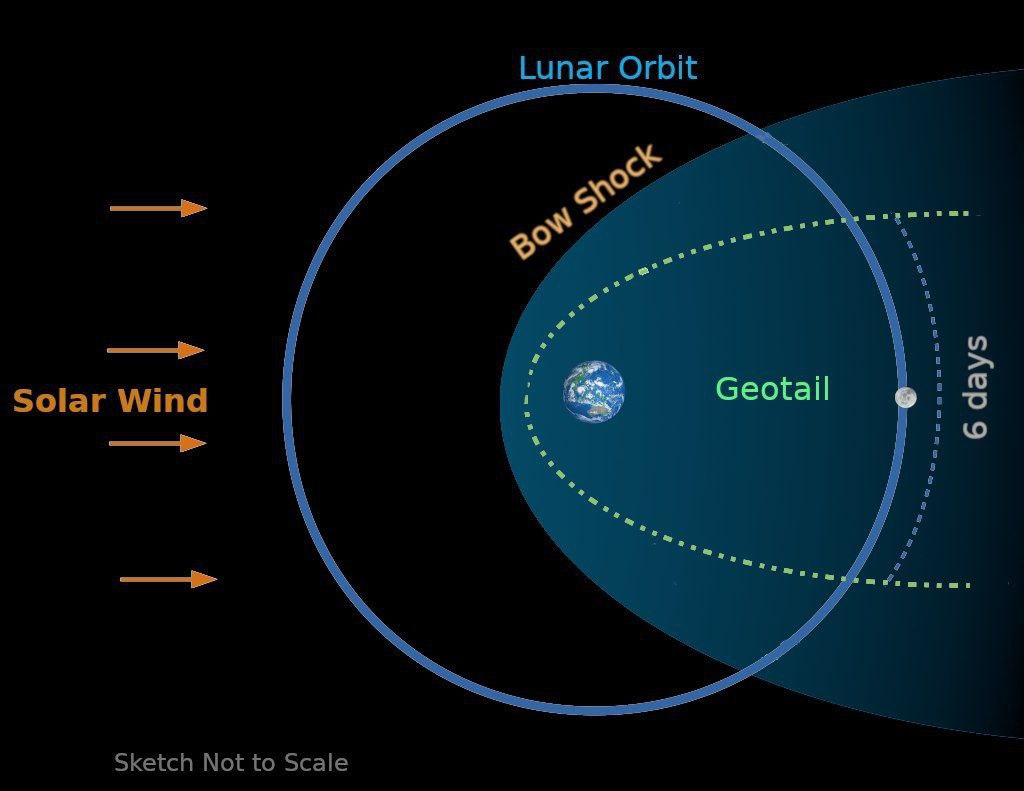
Our Sun emits a continuous outflowing stream of electrons and protons into the solar system, called the solar wind. The solar wind plasma which has charged particles embedded in the extended magnetic field of the Sun, moves at speeds of a few hundred km per second. It interacts with solar system bodies including Earth and its moon. Since the Earth has a global magnetic field, it obstructs the solar wind plasma and this interaction results in the formation of a magnetic envelope around Earth, called the magnetosphere.
The Earth’s magnetosphere is compressed into a region approximately three to four times the Earth radius (~22000 km above the surface) on the side facing the Sun, but is stretched into a long tail (geotail) on the opposite side that goes beyond the orbit of Moon. Approximately, once every 29 days, Moon traverses the geotail for about 6 days centered around full moon.
#Geo_Tail
#SOLAR_WIND












0 comments:
Post a Comment
We love hearing from our Readers! Please keep comments respectful and on-topic.